How to operate a drone safely and effectively is a question many aspiring pilots ask. This guide delves into the intricacies of drone operation, from understanding its fundamental components to mastering advanced flight techniques and adhering to crucial safety regulations. We’ll cover pre-flight checks, control mechanisms, navigation strategies, and even delve into the art of capturing stunning aerial photography and videography.
Whether you’re a complete beginner or seeking to refine your skills, this comprehensive resource will equip you with the knowledge and confidence to take to the skies responsibly.
We will explore the various types of drones available, their unique functionalities, and the specific considerations for each. The importance of understanding and complying with local laws and regulations will be emphasized throughout, ensuring your flights are both enjoyable and legally sound. We’ll also discuss troubleshooting common issues and maintaining your drone for optimal performance and longevity.
Drone Parts and Components
Understanding the individual components of a drone is crucial for safe and effective operation. This section details the function, importance, and potential issues associated with key drone parts, along with a comparison of different drone types and a guide to assembling a typical kit.
Drone Component Overview

The following table summarizes the key components of a typical multirotor drone:
| Component | Function | Importance | Potential Issues |
|---|---|---|---|
| Propellers | Generate thrust for lift and maneuverability. | Essential for flight; determines speed and efficiency. | Damage, imbalance, improper installation leading to vibrations or crashes. |
| Motors | Spin the propellers; controlled by the flight controller. | Provide power for flight; directly impacts flight performance. | Motor failure, overheating, malfunction due to water ingress or physical damage. |
| Flight Controller | The “brain” of the drone; manages motor speed, sensor data, and GPS. | Essential for stable and controlled flight; processes all flight data. | Software glitches, sensor malfunctions, physical damage affecting flight stability and control. |
| Battery | Provides power to all components. | Flight time is directly dependent on battery capacity and health. | Low voltage, cell imbalance, overheating, damage leading to reduced flight time or potential fire hazard. |
| GPS Module | Provides location data for autonomous flight and return-to-home functions. | Crucial for precise positioning and safe operation, especially in autonomous modes. | Signal loss, interference, inaccurate readings affecting positioning and flight stability. |
| Radio Transmitter & Receiver | Allows pilot control of the drone. | Essential for controlling the drone’s movements and functions. | Signal interference, low battery in the transmitter, range limitations leading to loss of control. |
| Camera (Optional) | Captures photos and videos. | Provides aerial photography and videography capabilities. | Malfunction, image quality issues, lens damage. |
Drone Type Comparison
Multirotor drones (quadcopters, hexacopters, octocopters) are the most common type, offering vertical takeoff and landing (VTOL) capabilities and excellent maneuverability. Fixed-wing drones, resembling airplanes, require a runway for takeoff and landing but offer longer flight times and greater range. Hybrid drones combine aspects of both, offering a balance of maneuverability and endurance.
Understanding drone operation involves mastering several key skills, from pre-flight checks to navigating airspace regulations. Successfully piloting a drone requires careful attention to detail, and a great resource for learning the fundamentals is available at how to operate a drone. This will help you confidently handle your drone, ensuring safe and effective operation. Ultimately, consistent practice and a solid understanding of the controls are crucial for proficient drone piloting.
Assembling a Drone Kit
Assembling a drone kit typically involves connecting the motors to the flight controller, attaching the propellers, and securing the battery. Detailed instructions are usually provided with the kit. Always follow the manufacturer’s instructions precisely.
- Carefully inspect all components for any damage.
- Connect the motors to the designated ports on the flight controller, ensuring correct orientation.
- Securely attach the propellers to the motors, paying attention to the direction of rotation.
- Mount the battery securely to the drone frame.
- Calibrate the flight controller according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
- Perform a pre-flight check (detailed in the next section).
Pre-Flight Checks and Procedures
A thorough pre-flight check is essential for safe and successful drone operation. This section Artikels the necessary steps to ensure your drone is ready for flight.
Pre-Flight Checklist
Before each flight, perform the following checks:
- Inspect the drone for any physical damage to propellers, motors, or frame.
- Ensure the battery is fully charged and shows no signs of damage or swelling.
- Check the connection of all components, including motors, battery, and flight controller.
- Verify that the radio transmitter is powered on and has sufficient battery life.
- Calibrate the drone’s compass and IMU (Inertial Measurement Unit).
- Check GPS signal strength and accuracy.
- Review weather conditions and ensure they are suitable for flight.
- Confirm that you are operating within legal airspace restrictions.
Sensor and Compass Calibration
Calibrating the drone’s sensors and compass is crucial for accurate flight and stability. This process ensures the drone understands its orientation and position correctly. Follow the manufacturer’s instructions for the specific calibration procedure for your drone model. This usually involves a series of specific movements to allow the sensors to self-orient.
Pre-Flight Battery Check
Check the battery voltage using a multimeter or the drone’s battery indicator. Ensure the voltage is within the acceptable range specified by the manufacturer. For multi-cell batteries, check for cell imbalance, where individual cells have significantly different voltages. An imbalanced battery can lead to poor performance and potential damage.
Controlling the Drone
Understanding the basic controls and flight modes is fundamental to operating a drone safely and effectively. This section explains the controls, different flight modes, and suggests a training exercise for beginners.
Basic Drone Controls
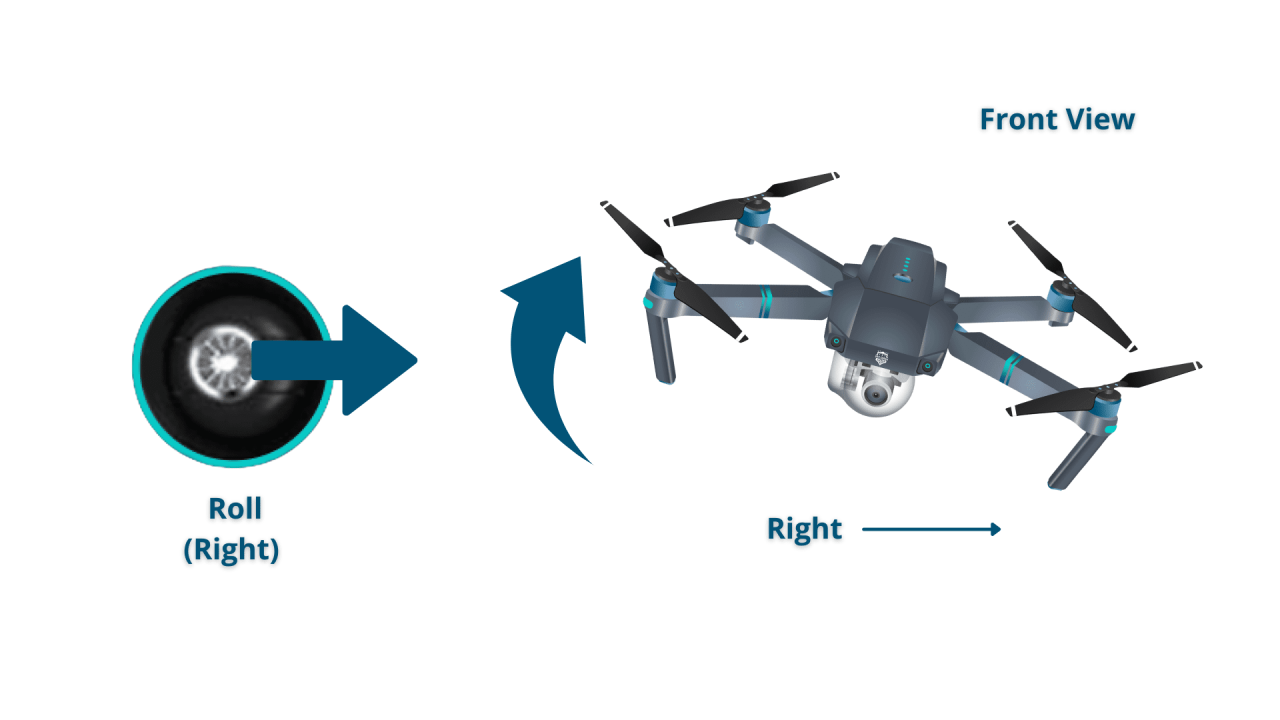
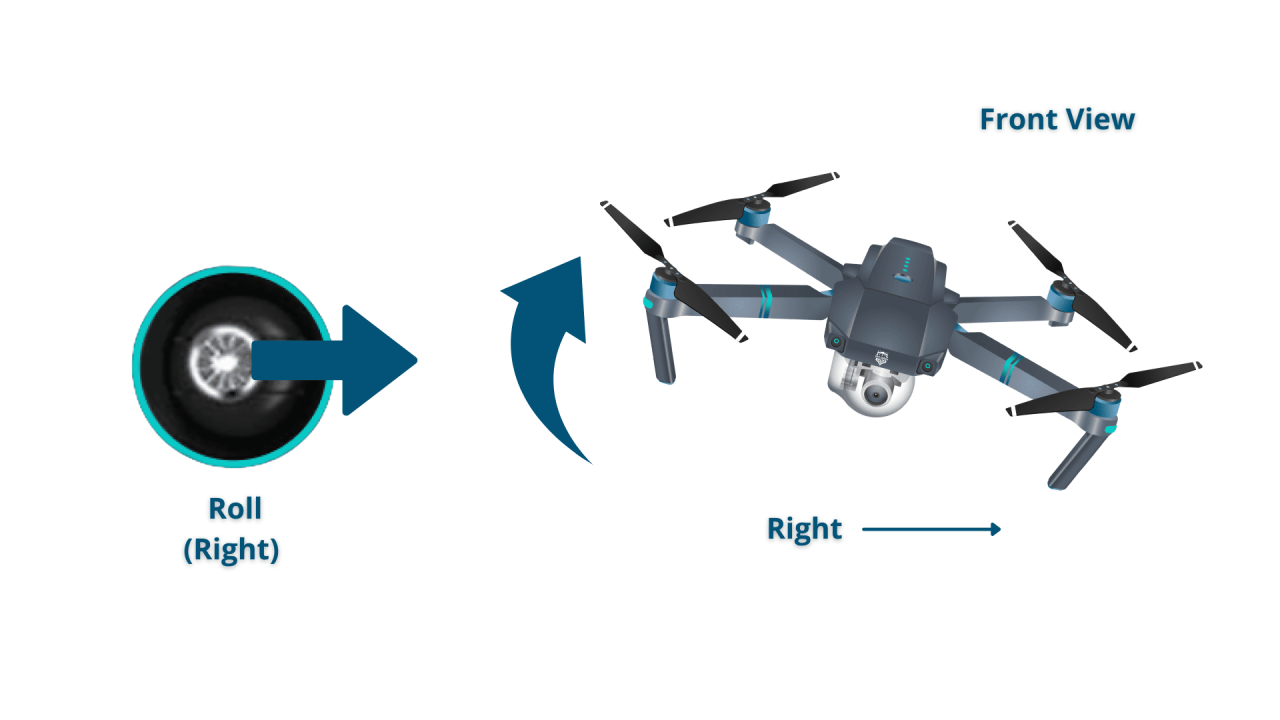
Most drones use two joysticks to control movement. One joystick typically controls throttle (up/down) and pitch (forward/backward), while the other controls roll (left/right) and yaw (rotation). The effects of each stick movement are illustrated below:
| Control | Joystick Movement | Effect on Drone |
|---|---|---|
| Throttle | Up: Increase altitude; Down: Decrease altitude | Ascend or descend |
| Pitch | Forward: Move forward; Backward: Move backward | Move forward or backward |
| Roll | Right: Tilt right; Left: Tilt left | Move right or left |
| Yaw | Right: Rotate clockwise; Left: Rotate counter-clockwise | Rotate around its vertical axis |
Flight Modes
Different flight modes offer varying levels of stability and maneuverability. Beginner mode limits speed and responsiveness, aiding stability. Sport mode allows for faster and more agile maneuvers, but requires more skill. Other modes might include GPS mode for autonomous flight or advanced modes for acrobatic maneuvers.
Basic Drone Maneuver Training

Practice the following maneuvers in a safe, open area, away from obstacles and people:
- Hovering: Practice maintaining a stable position in the air.
- Takeoff and Landing: Smoothly lift off and land the drone.
- Directional Movement: Practice moving the drone forward, backward, left, and right.
- Turning: Practice smooth turns using yaw control.
- Altitude Changes: Practice smoothly ascending and descending.
Navigation and Flight Planning
Effective navigation is crucial for safe and efficient drone operation. This section explores various navigation methods and flight planning tools.
Drone Navigation Methods
Drones can be navigated using several methods:
- GPS Navigation: Uses satellite signals for precise positioning and autonomous flight.
- Visual Navigation: Relies on the pilot’s visual observation of the drone’s position and surroundings.
- Waypoint Following: The drone automatically follows a pre-programmed series of waypoints.
Flight Planning Software and Apps
Several software applications and mobile apps facilitate flight planning. Each offers a different set of features and capabilities. The choice depends on individual needs and preferences.
| Software/App | Features | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|
| Litchi | Waypoint planning, autonomous flight modes, obstacle avoidance | Robust features, user-friendly interface | Can be expensive |
| DroneDeploy | Mapping, 3D modeling, data analysis | Powerful mapping capabilities | Steeper learning curve |
| DJI Fly | Simple waypoint planning, intelligent flight modes | Easy to use, integrated with DJI drones | Limited advanced features |
Creating and Following a Simple Flight Plan
Using an app like DJI Fly, you can create a simple flight plan by selecting waypoints on a map. The app will then guide the drone through the pre-defined route. Always review the planned route carefully before initiating the autonomous flight.
Drone Safety and Regulations
Understanding and adhering to drone regulations and safety procedures is paramount. This section discusses potential hazards and Artikels emergency procedures.
Drone Regulations and Airspace Restrictions, How to operate a drone
Always check and comply with local and national drone regulations before operating your drone. These regulations often include restrictions on airspace, flight altitude, and operational areas. Failure to comply can result in penalties.
Potential Hazards and Mitigation
Drone operation involves several potential hazards:
- Obstacles: Trees, buildings, power lines can cause collisions. Maintain visual contact and use obstacle avoidance features.
- Weather Conditions: Strong winds, rain, or snow can negatively impact flight stability and control. Avoid flying in adverse weather conditions.
- Battery Failure: Low battery can cause a sudden loss of power and a crash. Always monitor battery levels and plan for a safe return.
- Signal Interference/Loss of Signal: Interference or loss of signal can lead to loss of control. Operate within the transmitter’s range and be aware of potential sources of interference.
Emergency Procedures
| Scenario | Emergency Procedure |
|---|---|
| Loss of Signal | Activate Return-to-Home (RTH) function if available; attempt to regain signal; land the drone manually if possible. |
| Low Battery | Immediately initiate RTH or land the drone manually in a safe location. |
| Unexpected Malfunction | Attempt to regain control; if unsuccessful, initiate RTH or attempt a controlled emergency landing. |
Drone Photography and Videography: How To Operate A Drone
Drones offer unique perspectives for capturing stunning photos and videos. This section explains how to adjust camera settings and employ effective flight techniques.
Adjusting Camera Settings
Understanding aperture, shutter speed, and ISO is crucial for optimal image quality. Aperture controls depth of field, shutter speed controls motion blur, and ISO affects image noise. Experiment with different settings to find the best combination for your scene.
Flight Techniques for Aerial Footage
Capture compelling footage by using smooth tracking shots to follow subjects, dynamic circling for dramatic perspectives, and careful planning of your flight path to capture the best angles and compositions.
Tips for Composing Effective Drone Photos and Videos
- Plan your shots carefully, considering composition, lighting, and subject matter.
- Use the “rule of thirds” to create visually appealing images.
- Experiment with different angles and perspectives.
- Maintain smooth and controlled movements to avoid shaky footage.
- Edit your footage to enhance its visual impact.
Drone Maintenance and Troubleshooting
Regular maintenance and prompt troubleshooting are essential for prolonging the lifespan of your drone. This section provides guidance on maintenance and troubleshooting common issues.
Routine Maintenance Schedule
Regularly inspect your drone for physical damage, clean propellers and motors, and check for loose connections. Follow the manufacturer’s recommendations for specific maintenance tasks and intervals.
Troubleshooting Common Drone Issues
| Issue | Troubleshooting Steps |
|---|---|
| Motor Failure | Check motor connections; inspect for physical damage; replace faulty motor. |
| GPS Issues | Ensure clear GPS signal; recalibrate compass and GPS; check for software updates. |
| Connection Problems | Check transmitter and receiver batteries; ensure proper connection of all components; check for signal interference. |
Battery Care and Storage
Properly store and charge drone batteries to maximize their lifespan. Store batteries in a cool, dry place, away from direct sunlight. Charge batteries according to the manufacturer’s instructions, avoiding overcharging or deep discharging.
Mastering the art of drone operation is a journey of continuous learning and practice. From understanding the basic controls to executing complex maneuvers and capturing breathtaking visuals, this guide has provided a solid foundation. Remember that safety and adherence to regulations are paramount. By consistently practicing safe flight procedures and staying updated on relevant regulations, you can unlock the full potential of your drone while ensuring responsible and enjoyable aerial adventures.
Soar responsibly, and happy flying!
Understanding drone operation involves familiarizing yourself with its controls and safety protocols. Learning how to navigate the device effectively is crucial, and a great resource for this is available at how to operate a drone , which offers comprehensive guidance. Mastering these skills ensures safe and efficient drone operation, ultimately leading to a more enjoyable and productive experience.
Commonly Asked Questions
What is the best drone for beginners?
Several user-friendly drones are excellent for beginners, often featuring features like GPS stabilization and automatic return-to-home functions. Research reviews and consider factors like budget and desired features.
How long does a drone battery last?
Drone battery life varies significantly depending on the drone model, battery size, and flight conditions (wind, payload). Check your drone’s specifications for estimated flight times.
What happens if I lose signal with my drone?
Most modern drones have a return-to-home (RTH) function that automatically brings the drone back to its starting point if signal is lost. However, always fly within visual line of sight and in a safe, open area.
How do I register my drone?
Drone registration requirements vary by country and region. Check with your local aviation authority for specific regulations and registration procedures in your area.